The Health & Wellness Blog
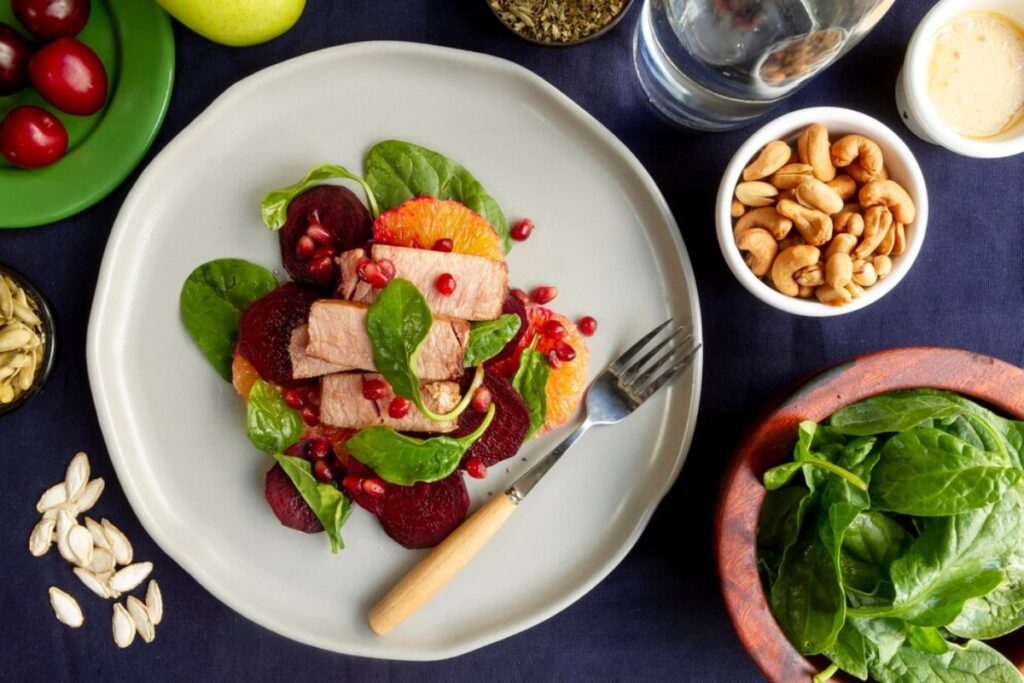

Dinner Recipes to Reduce Inflammation
Dinner is more than just the last meal of the day — it’s an opportunity to reset and refuel your body after everything it’s endured. Or an anti-inflammatory dinner can help you recover from stress, processed snacks or quick lunches. It helps your body relax naturally.
When you get it right, your evening meal isn’t merely about filling your belly. It can enhance sleep quality, ease digestion, and reduce the inflammation that accumulates from daily stressors. Inflammation-busting dinners are the ticket. They help with long-term health, hormonal balance, and less chronic pain.
Why Anti-Inflammatory Dinners Matter
Some actually don’t realise they consume inflammatory foods at dinner. These include refined carbs, processed meats and sugary sauces. Such foods make us bloated, uncomfortable and disrupt sleep. All of the above are symptoms of low-grade inflammation in your body.
Conversely, a dinner high in whole foods, omega-3s, fibre and antioxidants may do the contrary. It helps the body transition into rest and repair mode. Not to mention, it then primes you for better digestion and blood sugar control the next day.
Key Benefits of Anti-Inflammatory Evening Meals
1. Promotes Restful Sleep
A balanced dinner with magnesium, healthy fats, and complex carbs helps boost melatonin and serotonin production. These hormones are essential for deep sleep.
2. Supports Overnight Recovery
Nutrients like omega-3s and antioxidants aid muscle repair and tissue healing while you sleep.
3. Reduces Bloating and Discomfort
Anti-inflammatory ingredients can calm the digestive system. They also reduce gut irritation from heavy or fried meals.

4. Keeps Blood Sugar Stable
Whole foods help prevent the blood sugar spikes and crashes that interfere with metabolism and fat storage overnight.
5 Simple and Satisfying Anti-Inflammatory Dinner Recipes
1. Baked Turmeric Salmon with Roasted Vegetables
Ingredients:
- 1 salmon fillet
- 1 tsp turmeric
- ½ tsp garlic powder
- 1 tbsp olive oil
- Assorted vegetables: Brussels sprouts, sweet potatoes, and carrots
Why it works: Salmon is packed with omega-3 fatty acids, which fight inflammation at the cellular level. Turmeric, especially with black pepper, provides curcumin. Curcumin is one of the most researched anti-inflammatory compounds.
2. Stuffed Bell Peppers with Quinoa and Black Beans
Ingredients:
- Bell peppers (halved and seeded)
- 1 cup cooked quinoa
- ½ cup black beans
- Corn, tomatoes, onions, and avocado
- Cumin, chilli powder, and fresh lime juice
Why it works: Quinoa is a complete plant protein and high in fibre, while black beans add resistant starch and antioxidants. Peppers and tomatoes are rich in vitamin C and lycopene. Both are known to reduce inflammation.
3. Lentil and Spinach Coconut Curry
Ingredients:
- 1 cup cooked lentils
- 1 handful of spinach
- ½ can of coconut milk
- Garlic, ginger, turmeric, and curry powder
- Served with brown rice or cauliflower rice
Why it works: Lentils are rich in fibre and plant protein. Coconut milk provides healthy fats that soothe. Spices like ginger and turmeric add anti-inflammatory benefits and improve circulation.
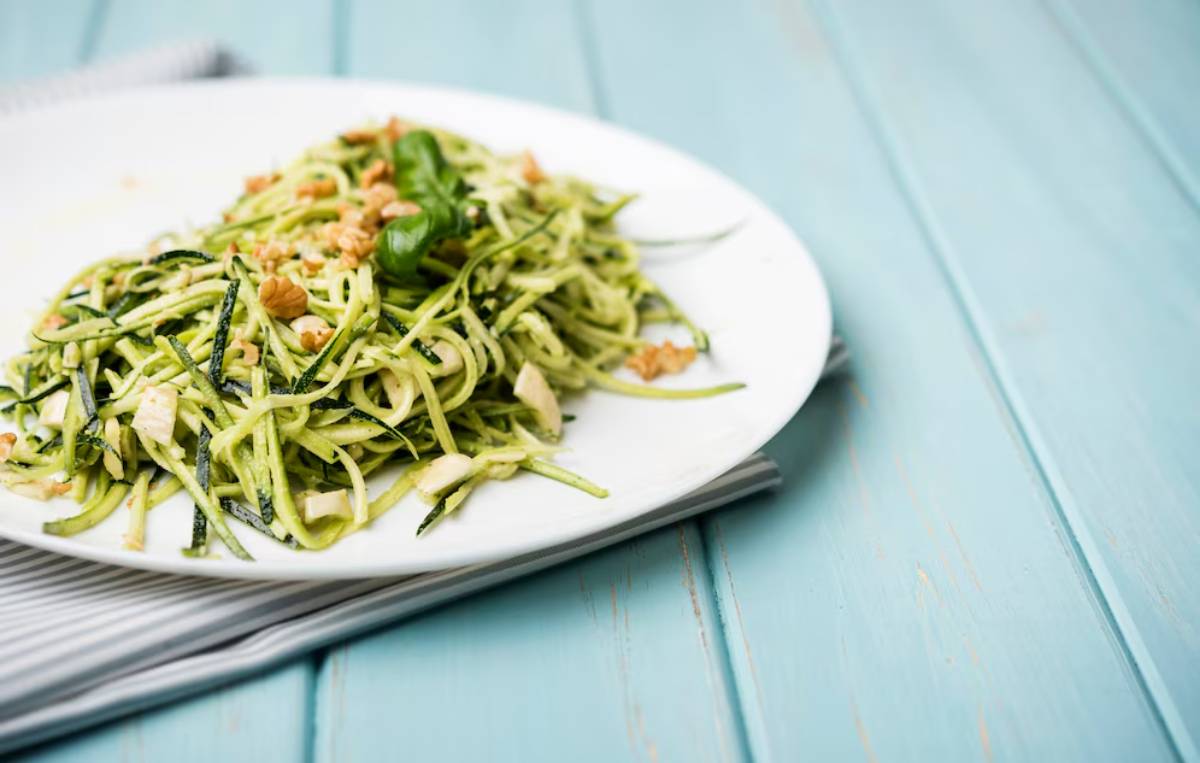

4. Zucchini Noodles with Pesto and Grilled Chicken
Ingredients:
- 2 zucchinis, spiralised
- Grilled chicken breast
- Homemade pesto (olive oil, basil, garlic, walnuts)
- Cherry tomatoes
Why it works: This light, low-carb dinner avoids blood sugar spikes and bloating. The pesto provides healthy fats, and chicken offers lean protein essential for tissue repair and muscle health.
5. Sweet Potato and Kale Sheet Pan Bowl
Ingredients:
- Cubed sweet potatoes
- Chopped kale
- Chickpeas
- Olive oil, garlic, rosemary, and a sprinkle of sea salt
- Tahini lemon drizzle
Why it works: This dish is high in beta-carotene, fibre, and plant-based protein. Kale supports liver detox pathways, and sweet potatoes are easy on the gut and naturally anti-inflammatory.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Your Evening Meals
Mistake #1: Eating Too Late
Late-night eating can interfere with digestion and sleep. Aim to eat dinner at least 2–3 hours before bed.
Mistake #2: Overloading on Carbs Without Fibre
Refined carbs like white rice or pasta can lead to blood sugar spikes, especially when eaten alone. Always pair them with fibre, protein, or healthy fats.
Mistake #3: Using Processed Sauces and Dressings
Many store-bought sauces have sugar, soybean oil, and preservatives. These can cause inflammation. Opt for homemade versions using olive oil, herbs, and spices.
Mistake #4: Ignoring Portion Balance
Even healthy meals can cause discomfort if too large or unbalanced. Keep portions of carbs, fats, and protein in check, and focus on how you feel after eating.
Expert Tips to Enhance Your Anti-Inflammatory Dinner Routine
Cook with Anti-Inflammatory Spices
Ginger, turmeric, rosemary, cumin, and cinnamon are more than tasty. They have compounds that lower inflammation and oxidative stress.
Choose the Right Cooking Methods
Grilling, roasting, steaming, and sautéing in olive oil keep nutrients better. This is more effective than deep-frying or overcooking. Avoid charring meats, which can create inflammatory compounds.
Use Seasonal Vegetables
Fresh, local produce contains more nutrients and fewer pesticides. They also vary your diet and introduce different antioxidant profiles.
Include Fermented or Probiotic Sides
Add a spoonful of sauerkraut, kimchi, or plain yogurt. These foods help balance gut bacteria. Balanced gut bacteria play a big role in controlling inflammation.
Advanced Insights: Science Behind the Plate
Omega-3s and Pro-Resolving Mediators
Omega-3 fatty acids (found in fatty fish, flaxseed, and walnuts) not only prevent inflammation, but they also help resolve it. They create pro-resolving mediators (SPMS). These SPMS signal the body to stop the inflammatory response when it’s not needed anymore.
The Gut-Immune Connection
Up to 70% of the immune system is located in the gut lining. A balanced anti-inflammatory dinner is high in fibre and low in processed foods. This helps gut health, which also supports immune regulation.
Timing Matters
Chrononutrition is the science of when you eat. It suggests that having a nutrient-rich dinner earlier in the evening fits better with your body’s natural rhythms. This may help reduce inflammation markers overnight.
Wind Down with Purposeful Nutrition
Dinner is not another item on your daily meal plan — it’s an opportunity to finish your day with relaxation, clarity and nourishment. Eating anti-inflammatory foods and cooking with intention allows your body to heal and rest.”
Loving a hearty lentil curry or an infused salmon veggie bowl? With each bite you are reducing silent inflammation that accumulates over time. With these simple, satisfying recipes, you’re not just having dinner — you’re making an investment in your long-term health.