The Health & Wellness Blog
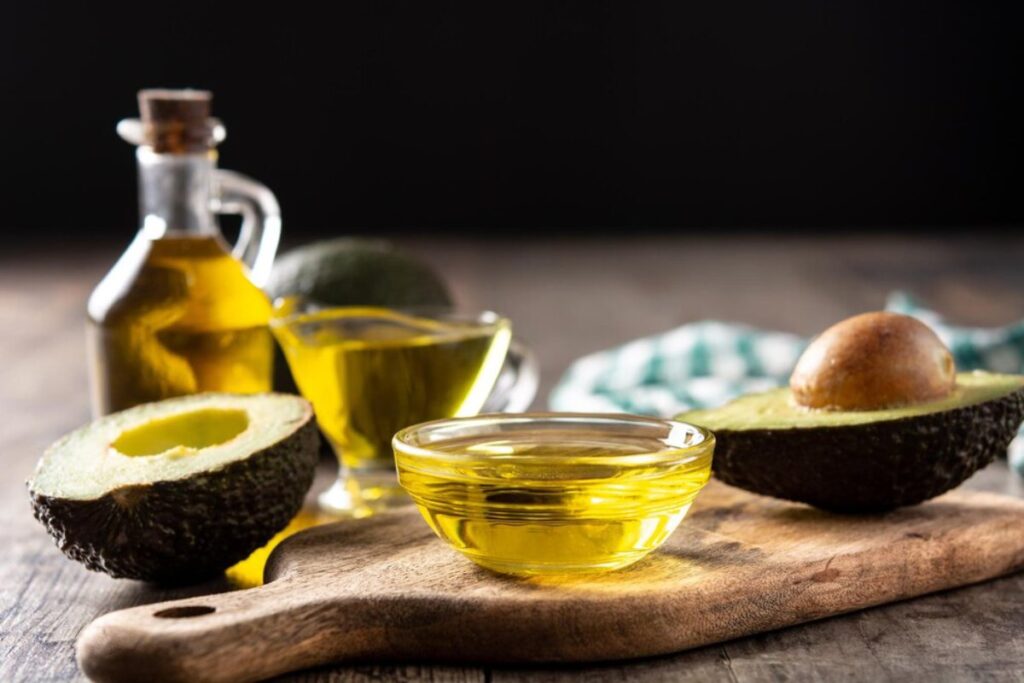

Healthy Fats and Oils for Inflammation Control
Everyone thinks about leafy greens, berries and turmeric when we talk about fighting inflammation through diet. But another nutritional powerhouse often flies under the radar: healthy fats. Some fats, including cold-pressed oils and omega-rich seeds, may help trim inflammation. They ensure long-term health, too.
Let’s look at what these fats do, what fats to focus on, and how to appropriately use them in your daily diet.
Why Inflammation Control Matters
Chronic inflammation is related to many serious health issues today. These include heart disease, arthritis, diabetes, Alzheimer’s, and some cancers. While inflammation is a natural response to injury or infection, problems arise when it becomes long-term and systemic.
The good news? Your diet can play a powerful role in regulating inflammation, and fats are a key part of that equation.
Understanding the Role of Healthy Fats
Fats Aren’t the Enemy
For decades, fats were unfairly demonised. But research has shown that not all fats are created equal.
How They Help
Healthy fats:
- Regulate inflammatory pathways at the cellular level
- Support hormone production and immune function
- Enhance absorption of fat-soluble vitamins like A, D, E, and K
- Help maintain brain, heart, and joint health
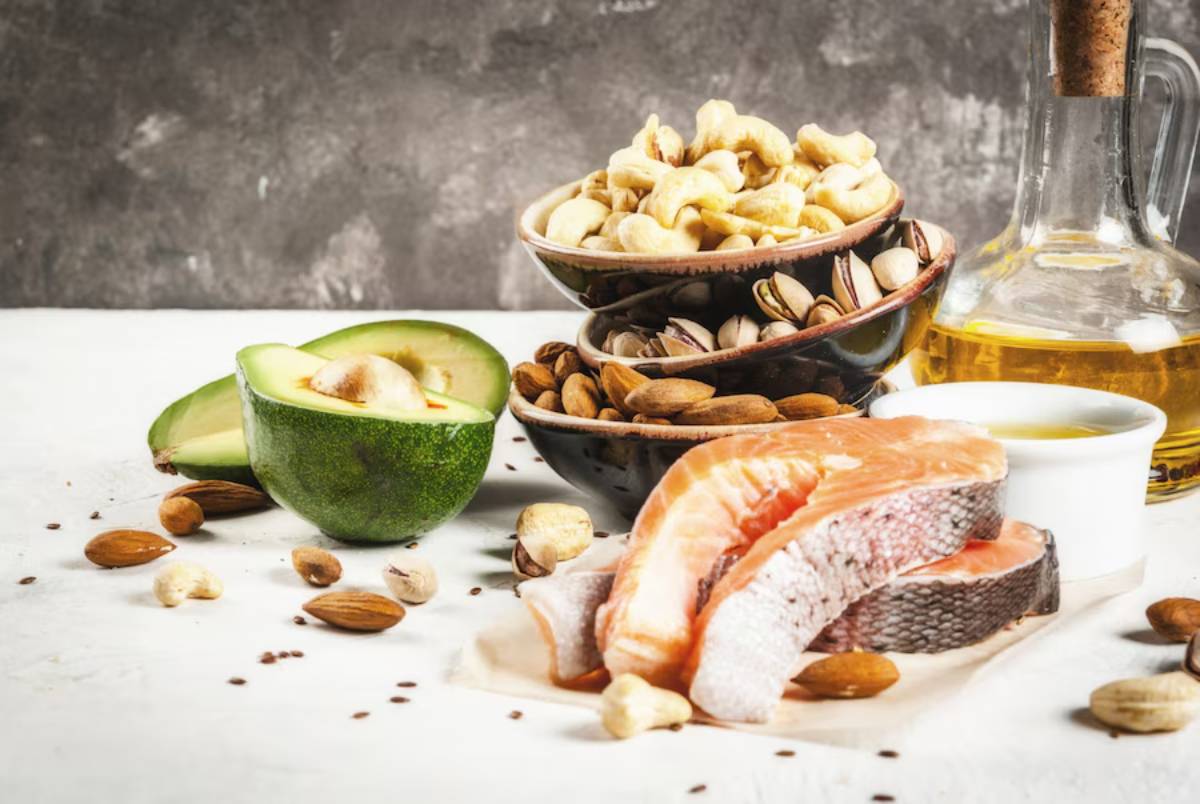

Key Anti-Inflammatory Fats and Oils to Include
1. Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Sources:
- Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines)
- Chia seeds
- Flaxseeds
- Walnuts
- Algal oil (for plant-based diets)
Why They Matter: Omega-3s are essential fatty acids that the body cannot produce on its own, they play a crucial role in reducing levels of inflammatory markers like C-reactive protein (CRP) and interleukin-6 (IL-6).
Pro Tip: Include 2–3 servings of fatty fish per week or add a tablespoon of ground flaxseed to your smoothies or oatmeal daily.
2. Extra Virgin Olive Oil (EVOO)
Why It’s a Star: Olive oil is high in monounsaturated fats and polyphenols. It can reduce inflammation like ibuprofen, but without the side effects.
How to Use It:
- Drizzle over salads or roasted vegetables
- Add to homemade vinaigrettes or dips
- Use as a finishing oil for soups and grains
Storage Tip: Keep it in a dark bottle away from heat to prevent oxidation.
3. Avocados and Avocado Oil
Nutritional Powerhouse: Avocados are loaded with monounsaturated fats, fiber, and antioxidants like lutein and beta-sitosterol, which may help lower CRP levels.
Culinary Uses:
- Spread on toast
- Toss into salads
- Blend into smoothies for creaminess
- Cook with avocado oil due to its high smoke point
4. Nuts and Seeds
Top Choices:
Walnuts (omega-3s)
- Almonds (vitamin E and monounsaturated fats)
- Pumpkin seeds (magnesium and zinc)
Snack Smart: Keep pre-portioned servings on hand for quick snacks or sprinkle on yoghurt, grain bowls, or sautéed greens.
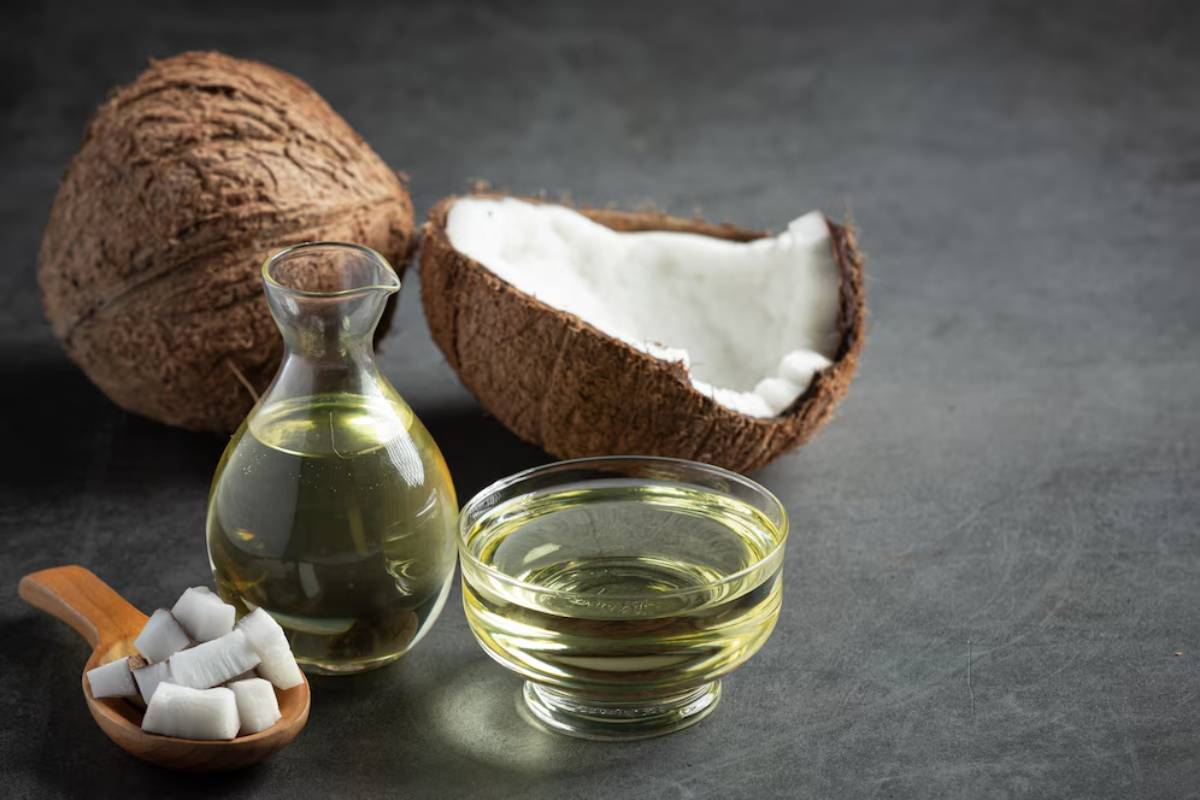

5. Coconut Oil – Use with Caution
While coconut oil has gained popularity, it’s high in saturated fats. Some studies suggest it may have a neutral or mildly anti-inflammatory effect, particularly when replacing processed fats. However, moderation is key.
When to Use It:
- Baking (as a butter substitute)
- Stir-frying (due to its stability at high heat)
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Mistake 1: Using Refined Vegetable Oils
Problem: Canola, corn, soybean, and sunflower oils are heavily processed and often high in omega-6 fatty acids, which can promote inflammation when consumed in excess.
Fix: Stick to cold-pressed, unrefined oils like EVOO, flaxseed oil (for cold dishes), or avocado oil.
Mistake 2: Ignoring Omega-6 to Omega-3 Balance
Why It Matters: The modern Western diet is disproportionately high in omega-6 fats compared to omega-3s. A better balance (closer to 2:1 or 4:1) supports reduced inflammation.
How to Improve It:
- Reduce intake of processed snacks and fried foods
- Increase fatty fish, flax, and chia in your meals
- Avoid margarine and hydrogenated oils altogether
Mistake 3: Overheating Healthy Oils
What Happens: When oils are heated beyond their smoke point, they break down and form harmful compounds.
Best Practices:
- Use olive oil for low-to-medium heat
- Reserve flaxseed oil for salad dressings only
- Use avocado oil or ghee for high-heat cooking
Advanced Insights and Expert Recommendations
Understanding the Science of Inflammation and Fat
Fats influence inflammation at the cellular membrane level. Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA, help produce resolvins and protectins—molecules that actively resolve inflammation. This explains why diets like the Mediterranean diet, rich in olive oil and fish, are associated with lower levels of chronic disease.

Expert Advice from Nutritionists
“A balanced intake of omega-3s and plant-based monounsaturated fats can help regulate the inflammatory response and support long-term wellness,” says Dr. Samantha Greene, integrative nutritionist.
“It’s not just about adding fats, but choosing the right kinds and pairing them with antioxidant-rich foods for a synergistic effect.”
How to Build a Fat-Smart, Anti-Inflammatory Plate
Morning
- Avocado on sprouted toast with chia seeds
- Oatmeal topped with walnuts and ground flax
Lunch
- Quinoa salad with EVOO dressing and grilled salmon
- Hummus and veggie wrap with sunflower seeds
Dinner
- Stir-fried vegetables in avocado oil with tofu
- Roasted sweet potatoes with olive oil and pumpkin seeds
Wrapping It Up: Fats That Heal, Not Harm
Good fats and oils control inflammation. They also promote brain health, heart function, hormonal balance, and more. Quality over quantity is the main thing. Add fatty fish to your plate, along with avocados, nuts and cold-pressed oils. Avoid relying too heavily on processed fats as well.
One ingredient can’t cure inflammation, but healthy fats are a potent and delicious place to begin.
Want to create a personalised anti-inflammatory eating plan? Let’s make one that fits in with your lifestyle and goals.