The Health & Wellness Blog

How to Maintain an Anti-Inflammatory Lifestyle
Genetics don’t have a huge influence, and living an anti-inflammatory lifestyle comprises much more than diet. It encompasses daily habits, stress management, movement and mindfulness. Chronic inflammation is associated with serious health problems such as heart disease, arthritis, diabetes, and some cancers. But there are certain lifestyle changes you can make to minimize inflammation and improve your health.
An anti-inflammatory lifestyle takes a whole body approach. Your body’s responses to inflammation are influenced by what you eat, how you move, how you sleep and your mindset. This guide will help you understand key concepts, learn a few easy-to-follow steps, and discover practices that enable an anti-inflammatory lifestyle both achievable and enjoyable.
Understanding the Core
Inflammation is your body’s natural defense. Acute inflammation helps heal injuries and fight infections. In contrast, chronic inflammation can harm tissues and lead to serious health problems.
Key contributors to chronic inflammation include:
- Processed and sugary foods
- Sedentary behavior
- Poor sleep quality
- High stress levels
- Environmental toxins
An anti-inflammatory lifestyle counters these issues by promoting healthier habits.
Key lifestyle factors include:
- Whole-food nutrition
- Regular physical activity
- Restorative sleep
- Stress management techniques
- Avoiding harmful chemicals
By focusing on these elements, you can build a strong foundation for health.
Quick Guide
Here’s a snapshot of actions to support an anti-inflammatory lifestyle:
- Choose whole, unprocessed foods rich in nutrients and fibre.
- Move your body regularly through walking, stretching, or workouts.
- Prioritise sleep and maintain a consistent bedtime routine.
- Manage stress with mindfulness, deep breathing, or journaling.
- Stay hydrated with clean, filtered water.
- Avoid smoking, excessive alcohol, and chemical-laden products.
Pro Tip: Start small. Add one new habit at a time, like including leafy greens in one meal or taking a short walk after dinner. Consistency is key.
Step-by-Step Guide
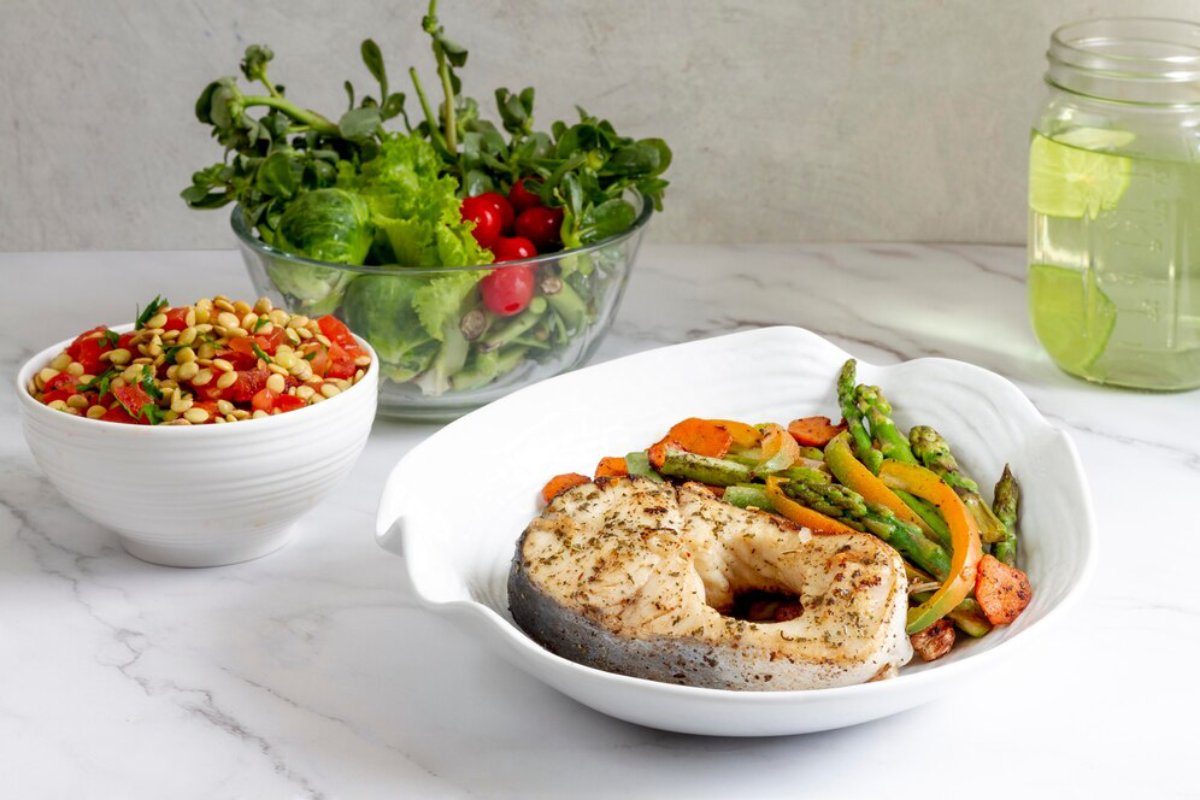

1. Clean Up Your Diet
Nutrition is crucial for fighting inflammation. Focus on these anti-inflammatory foods:
- Leafy greens (spinach, kale, arugula)
- Fatty fish (salmon, sardines, mackerel)
- Berries (blueberries, strawberries)
- Nuts and seeds (almonds, flaxseeds, chia seeds)
- Olive oil and avocado
- Spices like turmeric and ginger
Reduce or eliminate:
- Processed foods
- Refined sugars
- White flour and refined carbs
- Hydrogenated and trans fats
- Excessive alcohol
Important Tip: Batch cooking anti-inflammatory meals on weekends can save time during busy weeks.
2. Stay Active
Exercise reduces inflammation by improving circulation and helping the body process nutrients. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate activity most days.
Options include:
- Brisk walking
- Yoga or Pilates
- Strength training
- Swimming or cycling
Pro Tip: If time is tight, break the activity into shorter 10-minute bursts throughout the day.
3. Get Quality Sleep
Poor sleep increases inflammation and affects hunger and immunity hormones. Make sleep a priority by:
- Going to bed and waking up at the same time
- Limiting screen time 1–2 hours before bed
- Creating a cool, dark, quiet sleep environment
- Avoiding caffeine and alcohol late in the day
4. Manage Stress
Chronic stress triggers inflammation. Regular stress-reduction practices can help:
- Meditation or deep breathing
- Gratitude journaling
- Spending time in nature
- Creative outlets like art or music
Pro Tip: Take three deep belly breaths when feeling overwhelmed. It’s a fast way to signal safety to your nervous system.
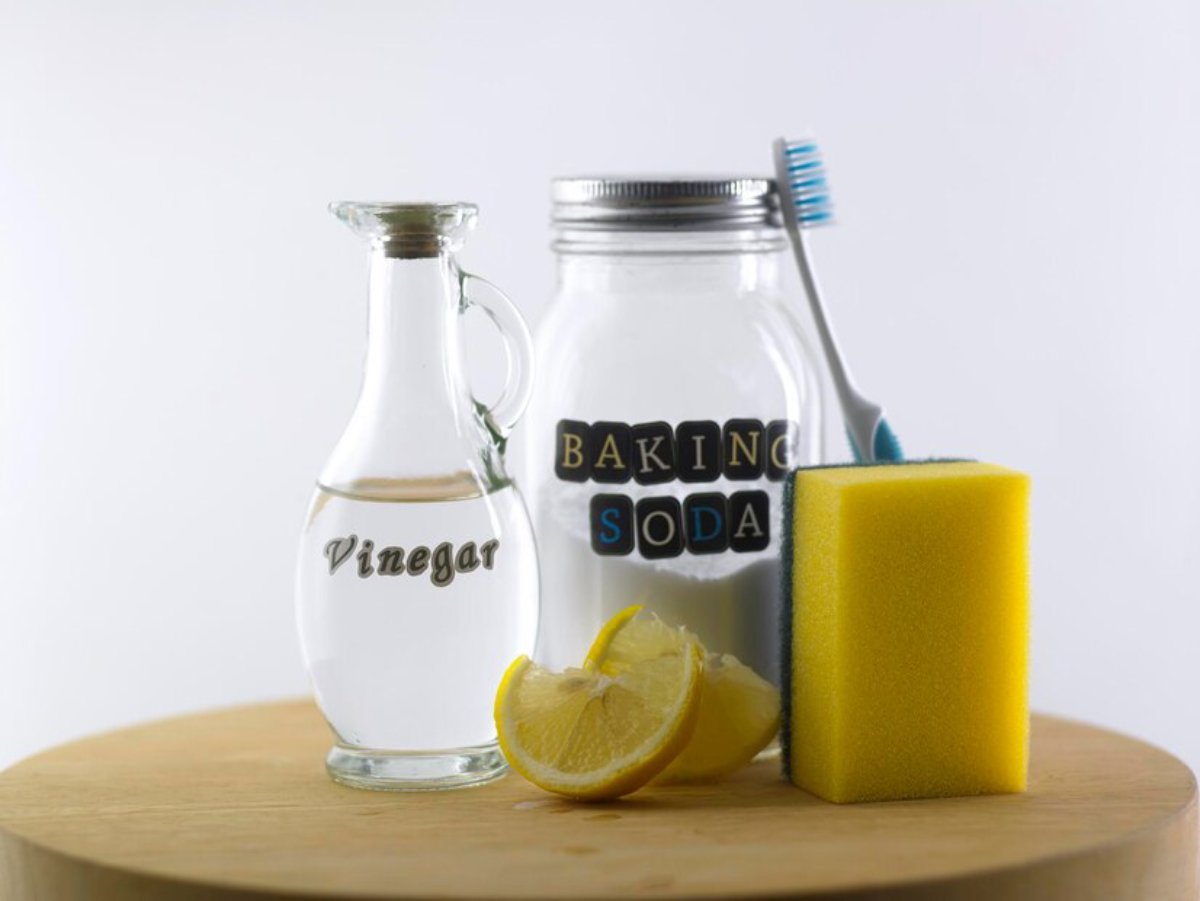

5. Reduce Environmental Toxins
Every day exposure to harmful chemicals can fuel inflammation. Choose:
- Natural cleaning solutions (vinegar, baking soda)
- Fragrance-free personal care products
- Glass or stainless-steel food containers
- Organic produce when possible
Important Notes
- Stay Patient: Results from lifestyle changes take time. Improvements may show as better energy, digestion, mood, and fewer aches.
- Personalisation Matters: Everyone responds differently. Some thrive on a Mediterranean diet, while others may prefer gluten-free or plant-based options. Track how your body reacts and adjust as needed.
- Hydration Is Key: Water is vital for cellular processes. Aim for at least 8 cups a day, more if active or in a hot climate.
- Supplements: Food should be your main nutrient source. However, supplements like omega-3s, vitamin D, and magnesium may offer added benefits. Always consult your healthcare provider before adding supplements.
Best Practices and Additional Insights
- Meal Planning: Plan meals and snacks around anti-inflammatory ingredients to avoid processed foods.
- Social Connections: Positive relationships and community engagement help lower stress and support health.
- Routine Check-ins: Keep a wellness journal to track food, sleep, stress, and movement. This helps you identify what’s working and what needs adjustment.
- Limit Screen Time: Excessive digital use, especially before bed, can impair sleep and increase stress. Set boundaries for tech use throughout the day.
Pro Tip: Use blue light filters on devices or wear blue-light blocking glasses if you work late.

FAQs
What is the fastest way to reduce inflammation in the body?
Focus on hydration, cut out processed foods, prioritize sleep, and engage in light exercise like walking or stretching.
Can lifestyle changes alone control chronic inflammation?
Yes, but if you have a diagnosed inflammatory condition, lifestyle changes should complement medical treatment, not replace it.
How do I know if I have chronic inflammation?
Symptoms can be subtle, including fatigue, joint pain, digestive issues, brain fog, and frequent colds. Blood tests like CRP can help detect inflammation.
Are anti-inflammatory diets restrictive?
Not at all! An anti-inflammatory diet is colorful, flavorful, and diverse. Enjoy a wide range of fruits, vegetables, healthy fats, proteins, and herbs.
Can stress really cause inflammation?
Absolutely. Chronic stress keeps cortisol levels high, disrupting immune function and contributing to inflammation.
Building a Lifestyle That Supports Long-Term Wellness
Living an anti-inflammatory lifestyle is a matter of making small, daily decisions that compound over time to produce big health results. It’s not a crash diet or a shortcut. It’s a promise to nurture your body, mind and environment in a way that helps to tamp down inflammation and pump up our vitality.
You lay the groundwork for lifelong wellness when you nourish yourself with whole foods, move regularly, sleep well and manage stress. Remember, progress is all about you. Go easy on yourself as you adjust to habits that promote your health.
If you’re starting over, pick one new habit today. Let that small step be the first step towards inflammation control and a brighter, healthier life on your path.